
Visit Our Sponsors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
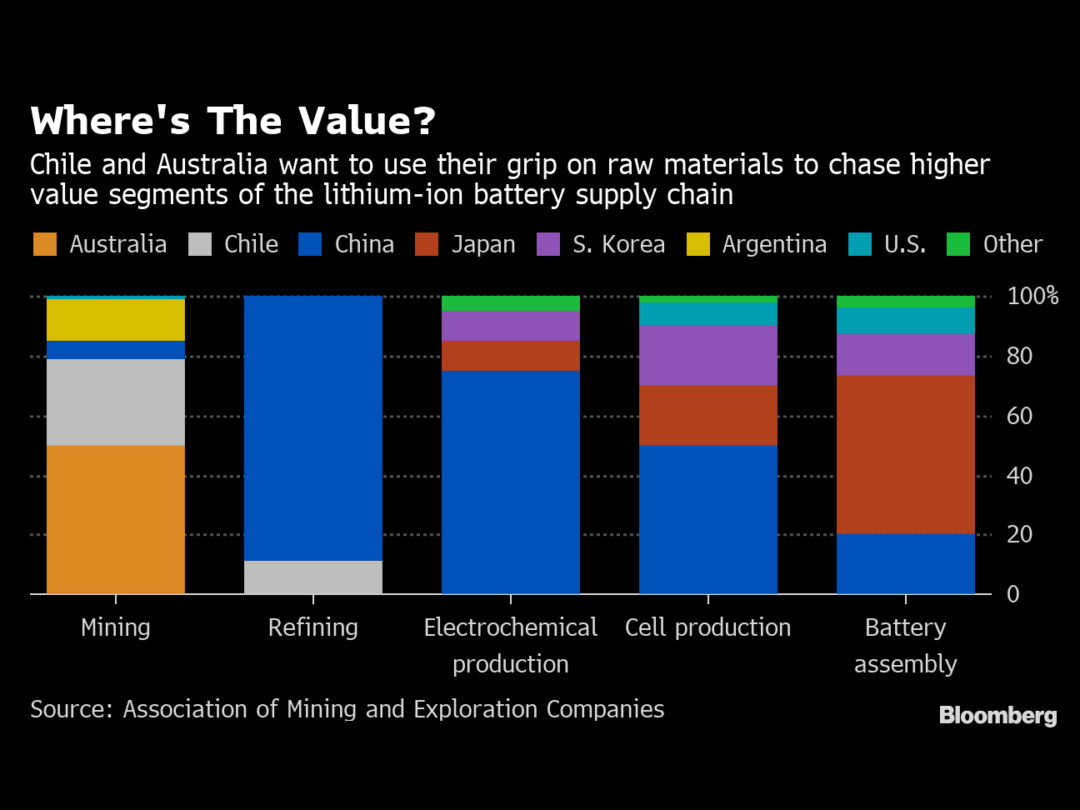
The race by Tesla Inc., Samsung SDI Co. and other technology giants to secure supplies of lithium — a key ingredient in batteries for electric vehicles and smartphones — is creating a unique chance for two global mining superpowers to reap more value from their natural resources.
Australia and Chile are looking to lithium to help them escape a cycle that for decades has had the two nations digging out minerals such as iron ore and copper, only to see them refined and turned into valuable products abroad.
Almost three-quarters of the world’s lithium raw materials come from mines in Australia or briny lakes in Chile, giving them leverage with customers scrambling to tie-up supplies. The mining nations hope to bring refining and manufacturing plants that could help kickstart domestic technology industries.
The first moves in that plan are beginning to take shape.
Scraping a shovel into a patch of dirt near the Australian port city of Bunbury in March, an executive for U.S.-based lithium leader Albemarle Corp. heralded a A$1bn ($690m) plan to build the world’s biggest processing plant of its type. Meanwhile, in Mejillones, northern Chile, South Korea’s Samsung SDI and Posco are planning to jointly develop a facility to make chemical components used in batteries.
“Chile and Australia have the advantage,” said Daniela Desormeaux, chief executive officer at Santiago-based consulting firm SignumBOX. They have the lithium and “at the same time state incentives, so companies transforming the raw material can set up shop there."
Mining rock and exporting it is a familiar story for Australia and Chile. Australia, the world’s biggest producer of iron ore, has shipped billions of tons of the steelmaking raw material to mills in Japan and China since the 1960s. Chile, the world’s largest source of copper, exports over half of its shipments as semi-refined concentrate.
“It’s an interesting economic model,” Peter Klinken, chief scientist of Western Australia and an adviser to the state’s government, told a February conference in Perth. “Take a big rock, make a little rock, put it on a ship, and then buy something really expensive back in return.”
The supply of lithium-ion batteries will need to jump more than 10-fold by 2030, BloombergNEF forecasts, with electric vehicles to account for more than 70 percent of that demand. That’s prompting end users to act, and Volkswagen AG and Volvo Cars have both struck long-term supply deals since April.
Where's the Value?
The first step on the lithium value ladder is refining the raw material, something that’s currently done mostly in China. Ore from mines or lithium-rich saline solution from underground lakes in South America is concentrated into a silvery-gray powder that is sent to be purified and refined into lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate. Those chemicals in turn are processed with materials such as nickel or cobalt to produce battery electrodes, or with solvents to make electrolytes, the key parts of the cells that are assembled into batteries.
Each step up the ladder affords more opportunity for profit. By 2025, the market for mined lithium raw material may be worth $20bn, compared with $43bn for refined products and $424bn for battery cells, according to a base case scenario outlined in a 2018 study published by the Australia-based Association of Mining and Exploration Companies.
Two major lithium miners operating in Chile, Sociedad Quimica & Minera de Chile SA, or SQM, and Albemarle were only allowed to expand production on condition that they sell a quarter of their output at the lowest market price to companies that will develop the materials within the country. SQM, which already carries out some processing in Chile, is expanding its domestic capacity.
The strategy is “a golden key” to build a higher-value lithium industry in Chile, said Sebastian Sichel, executive vice president of government development agency Corfo, which owns the lithium concessions in the Atacama desert and issues licenses to miners.
Three separate groups — Chile’s Molibdenos y Metales SA, or Molymet, China’s Sichuan Fulin Industrial Group Co., and a consortium of Samsung SDI and Posco — last year pledged to invest a total of about $754m to build lithium-cathode and lithium-cell factories in Chile to win access to Albemarle’s material. A second auction in April offered similar access to SQM’s product, with winners expected to be announced early next year.
New refining and chemical production capacity will offer Chile additional revenue, while earnings from lithium exports are also forecast to rise. The commodity has the potential to become one of the country’s largest exports after copper, salmon and wine, Sichel said.
Australia could generate more than A$50bn ($35bn) in annual revenue and support about 100,000 jobs by developing a battery materials sector, according to a 2018 study for a regional development agency. That compares with about A$1bn currently in annual lithium exports. Australia’s government in April pledged A$25m to support a five-year research program to expand its battery supply chain.
China’s Tianqi Lithium Corp. will later this year begin selling lithium hydroxide from a new processing facility in Kwinana, south of Perth. Tesla, battery maker LG Chem Ltd. and Mitsui & Co. have agreed to supply deals for output from a rival plant nearby that’s being built by Chile’s SQM and an Australian partner.
Efforts by Australia and Chile to wrest more control over refining from China are being helped by trade tensions. “They could definitely challenge China” in the next-step processing of lithium, said James Jeary, an analyst at CRU Group in London. Lithium producers will increasingly integrate mining and refining capacity, he said.
“We are hearing more and more that diversity of supply is critical,” said Phil Thick, Tianqi’s general manager in Australia. The producer’s Kwinana plant will mainly supply customers in North America and Europe, or carmakers in those regions via their suppliers in South Korea and Japan, he said.
China's in Charge
The producers plan to do more than just first-stage refining. Western Australia has developed a “Lithium Valley” strategy to span the supply chain. Chile also hopes to manufacture battery cells.
But there are major hurdles. Neither country has a major car industry, and the auto sector typically prefers component suppliers to be close to manufacturing hubs. The technical challenge of producing battery components may require imported expertise. Costs and environmental concerns are also factors.
A dispute between Corfo and Albemarle has already delayed progress for Molymet, the Samsung SDI and Posco consortium, and Sichuan Fulin in Chile, prompting concern the groups could opt to invest in battery projects elsewhere. In Australia, lithium producer Neometals Ltd. has delayed a plan to build a refinery, citing higher-than-expected costs. There may only be a brief window for Chile or Australia to get a foothold in the battery industry as rival mining nations join the fray.
Argentina and Bolivia have saline deposits near the border with Chile. Countries from Serbia to Mali are keen to extract deposits in their territory, and Russia, which has been producing lithium products for more than 60 years for its nuclear industry, is already trying to attract higher-value investment by setting up one of the world’s largest lithium-ion battery plants in Novosibirsk with Chinese partner Thunder Sky Group.
Persuading battery makers to set up operations in Australia or Chile will require state incentives, said Vivas Kumar, a principal consultant at industry adviser Benchmark Mineral Intelligence and previously a member of Tesla’s battery supply chain team.
Lowering the cost of battery cells “continues to be the most important focus area across all major companies,” Kumar said. Automakers “are increasingly becoming involved with their cell manufacturing partners’ supply chains in recognition of this.”
Sichel at Corfo believes lithium offers Chile a chance to escape the so-called resources curse, where mineral booms suck in investment at the expense of manufacturing.
If we don’t do this, “there is a gigantic risk that our growth keeps depending on the next hot commodity,” he said. “We remain stuck, unable to make the jump to developed-nation status.”
RELATED CONTENT
RELATED VIDEOS
Timely, incisive articles delivered directly to your inbox.






