
Think Tank
The Potential Impact of a Carbon Levy on Shipping Costs

The year 2020 has been one of unexpected change for the maritime space. On Jan. 1, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) began enforcing a new regulation (IMO 2020) that caps the allowable sulfur content of all global fuel oil used in ships from its former level of 3.5% m/m (mass/mass) to 0.5% m/m.
The action led to a flood of traders chartering vessels for floating storage, and high volatility in charter prices. Between March and May of 2020, one-year very large crude carrier (VLCC) rates increased 100%. The spot rate was even more volatile, with the TD1 route (Arabian Gulf to U.S. Gulf Coast) seeing over a 500% increase.
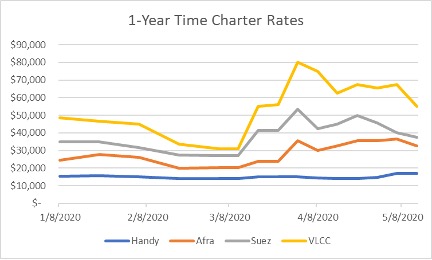
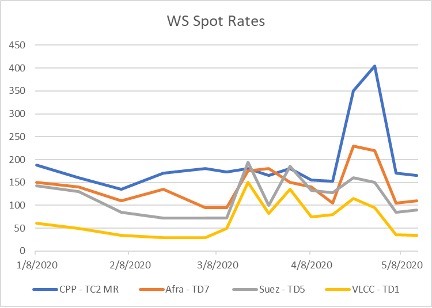
(Source: Alibra Shipping Limited)
The most recent wave of change came in the form of a proposal to the IMO from Trafigura, introducing a carbon level of between $250 per metric ton and $300/mt of CO2 equivalent on shipping fuels.
What would the impact of this proposal be to the oil industry if this carbon levy were instituted? According to Reuters, in 2018, the shipping industry was responsible for over 1 billion tons of CO2 emissions. Based on statistics from the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, crude oil accounts for 17% of maritime cargo. This would imply that crude oil shipping is responsible for roughly 179,520,000 tons of CO2 emissions.
In 2018, 1.886 billion tons, or 13,824 million barrels (bbls) of crude oil, were transported via ship. Considering that the proposal has an undefined benchmark at which the levy would be applied, it’s not exact math, but even if only 20% were applied, a VLCC voyage would have cost up to $1.5 million more. Given today’s VLCC rates, a 30-day voyage only costs about $900,000 for freight only.
|
2018 Shipping Data |
|
|
Total Emissions |
1,056,000,000 tons |
|
Crude Oil Share of Shipping |
17% |
|
Crude Oil Shipping Emissions |
179,520,000 tons |
|
Crude Oil Shipped (tons) |
1,886,000,000 tons |
|
Crude Oil Shipped (bbls) |
13,824,380,000 bbls |
|
Potential Impact |
@ $250/ton |
@ $300/ton |
|
20% Levy Cost per BBL |
$ 0.65 |
$ 0.78 |
|
VLCC Impact at 20% |
$ 1,298,575 |
$ 1,558,290 |
(Source: Opportune LLP)
In 2019, there were about 7,400 crude oil tankers in use globally, of which only about 175 are LNG-fueled vessels (just under 2.5%). The Trafigura proposal would impact 97% of the oil tanker fleet, and give any owners or charters of LNG-fueled vessels a significant competitive advantage in the market. While these levies will be assessed to the ship owner, it’s all but certain that they will be passed along to any charterers. Ultimately, freight rates will be market driven, so this levy would be an additional hurdle for those owners using fuel with greater emissions. All of this results in increased cost to the end consumer.
Steering Toward Renewables
More energy companies are turning their focus to clean and renewable energy options. Companies like BP, Shell, and Total have invested close to $10 billion in renewable energy projects. While these investments have low initial returns, a proposal of a levy on high-carbon fuels, while providing subsidies for low-carbon fuels, may be a bit like Robin Hood — robbing from traditional fuel oils to pay for their replacements and ultimate demise. It’s also interesting to note that the company proposing the high-carbon fuel levy recently announced plans to invest $2 billion into renewable energy projects.
What Are the Options for Low-Carbon Fuels?
- LNG: Liquified natural gas (LNG) is a proven and available commercial solution. In recent years, both Shell and ExxonMobil have invested in projects to provide LNG bunker fuels. There are currently more LNG-fueled ships under construction than there are in production, but it’s still a small percentage of total shipping capacity. While LNG has been hailed as the best fuel to meet the IMO 2020 regulations, there are concerns about how “green” LNG really is.
- Hydrogen: Shell recently published a report suggesting that liquid hydrogen was advantageous over other potential zero-emission fuels.
- Biofuel: In September, ExxonMobil completed a successful sea trial using marine biofuel oil. Both hydrogen and biofuel offer promise, but it hasn’t been as fully developed as LNG, so there’s still research to be done.
Regardless of the decision related to the carbon levy proposal, history has shown that the maritime industry will face new challenges each year. New regulatory changes will come, and with them a continued need for companies to be able to timely and accurately track and report their voyages, fuel usage and emissions. What will the next wave be?
James Morgan and James (Jay) Campbell are directors in the Process & Technology practice of Opportune LLP, a global energy business advisory firm.






